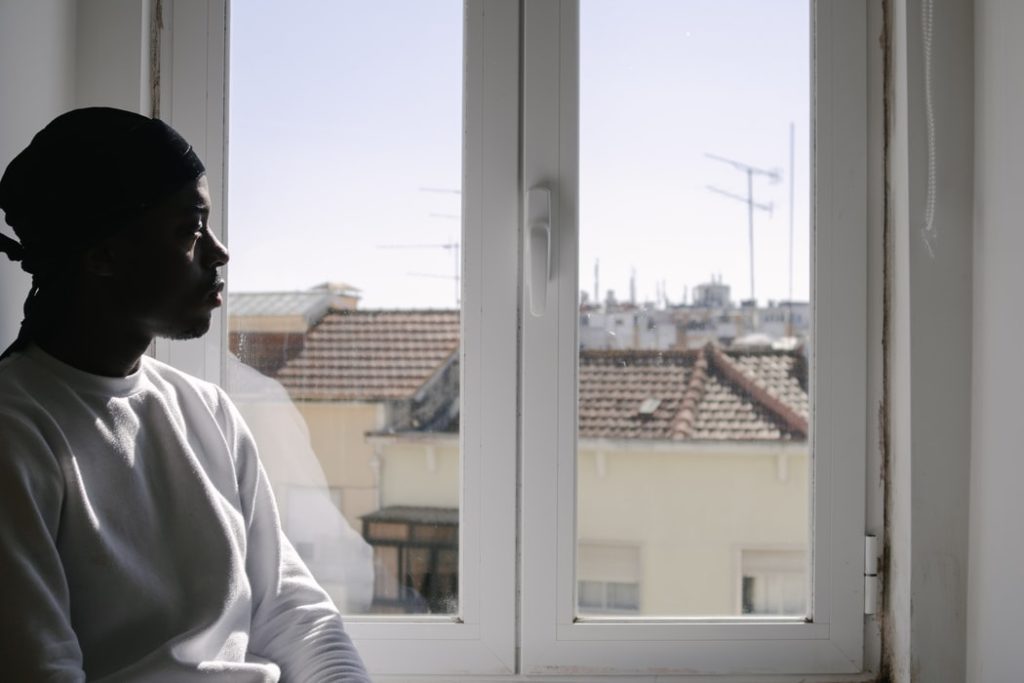
Depression is a leading cause of disability around the world. More than 264 million people suffer from this common mental health disorder.
Most people know that depression can leave an individual feeling tired, sad, hopeless, and uninterested in activities they used to enjoy. However, it isn’t as well-known that depression can have a physical impact on the brain itself.
Researchers are still working to understand exactly how depression affects the brain. At this point, though, it’s clear that depression can harm the brain’s physical structure.
Let’s take a look at what is known about depression and the brain.
How Depression Affects the Brain Physically
It is common knowledge that depression affects individuals on a psychological level. However, many people might not realize that depression can cause physical changes in the brain. These physical alterations to the brain can affect how an individual feels, acts and thinks.
Researchers aren’t exactly sure why these changes occur, but stress, genetics, and inflammation are thought to play a role.
Inflammation of the Brain
Some studies have found that long-term depression can lead to brain inflammation. It seems as though the length of time a person experiences depression is correlated with how much inflammation they have. What this means is that inflammation is much more likely in individuals that suffer from persistent depressive disorder.
Researchers are not sure whether inflammation leads to depression or vice versa. They are fairly certain that there is a connection between the two, though.
Brain inflammation can lead to the death of brain cells. This can cause several complications, including:
- Brain shrinkage
- Reduced function of neurotransmitters
- Decreased neuroplasticity
These complications can create problems with learning, memory, brain development, and mood.
Oxygen Restriction
Researchers have also found some evidence to suggest a connection between reduced oxygen in the body and depression. Inflammation, brain cell injury, and brain cell death can result from the brain not getting as much oxygen as it needs to function properly.
Connective and Structural Changes
Connective and structural changes can also occur in the brain when a person is suffering from depression. Some of the ways that a brain can change resulting from depression include:
- Reduction in the function of the hippocampus, which can lead to memory loss
- Reduction in the function of the amygdala, which can impact mood and emotional regulation
- Reduction in the function of the prefrontal cortex, which can affect executive function and attention
It generally takes at least eight months for changes likely to develop.
Brain Shrinkage
When a person experiences depression, it can actually lead to specific brain regions decreasing in size. However, at this point, there is a lot of ongoing debate about this topic. There is no hard and fast consensus over which regions of the brain decrease in size and how much they shrink when they do.
It is generally thought that the following parts of the brain have the potential to shrink when a person suffers from depression:
- Frontal lobe
- Hippocampus
- Prefrontal cortices
- Thalamus
How much shrinkage different regions of the brain experience due to depression depend on both the depressive episode’s severity and length.
Depression and the Brain: How It Impacts Cognitive Abilities
Depression can interfere with an individual’s ability to think clearly. Some researchers believe that an interruption of the brain’s chemical messengers or a reduction in their number could cause depression. This can also lead to impairment of cognitive function.
Attention
People who experience depression often also have co-occurring mental health issues. One commonly co-occurring mental health disorder is attention deficit disorder. Attention problems are also more common among people with depression than the general population.
It isn’t entirely clear why people with depression are more likely to have issues with attention. However, these two mental health issues are somehow linked.
Medications prescribed for depression can also create cognitive side effects. If you notice a sudden onset of attention issues or other cognitive problems, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor.
Are you interested in non-drug treatments for depression? If so, you can learn more about transcranial magnetic stimulation here.
Memory
How does depression affect memory?
A fairly common symptom of depression is memory loss. One study found that people suffering from depression had difficulty identifying identical objects or similar to other objects they had just seen a few moments prior. There was also evidence from a 2015 study that depression might cause short-term memory loss in some cases.
Executive Function
Your ability to complete simple tasks can be interrupted by executive function impairment. It can become nearly impossible to do things like paying bills or calling someone back.
Decision Making
When you are suffering from depression, it can be difficult to make even the smallest decisions. Agonizing indecision can result from questions as seemingly simple as where to go to dinner.
Are You Looking For Alternative Treatments to Depression?
Many people choose to take the medication to reduce the symptoms they experience from depression. However, these medications often have negative side effects or aren’t effective for certain individuals.
Now that you’re more familiar with how depression affects the brain, it can help you understand just how important it is to treat depression when you are suffering from it. Are you interested in TMS treatment for depression? If so, contact us today for more information or to schedule an appointment.